Zero Copy
Normal I/O
#include <unistd.h>
/* POSIX.1-2001, SVr4, 4.3BSD */
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
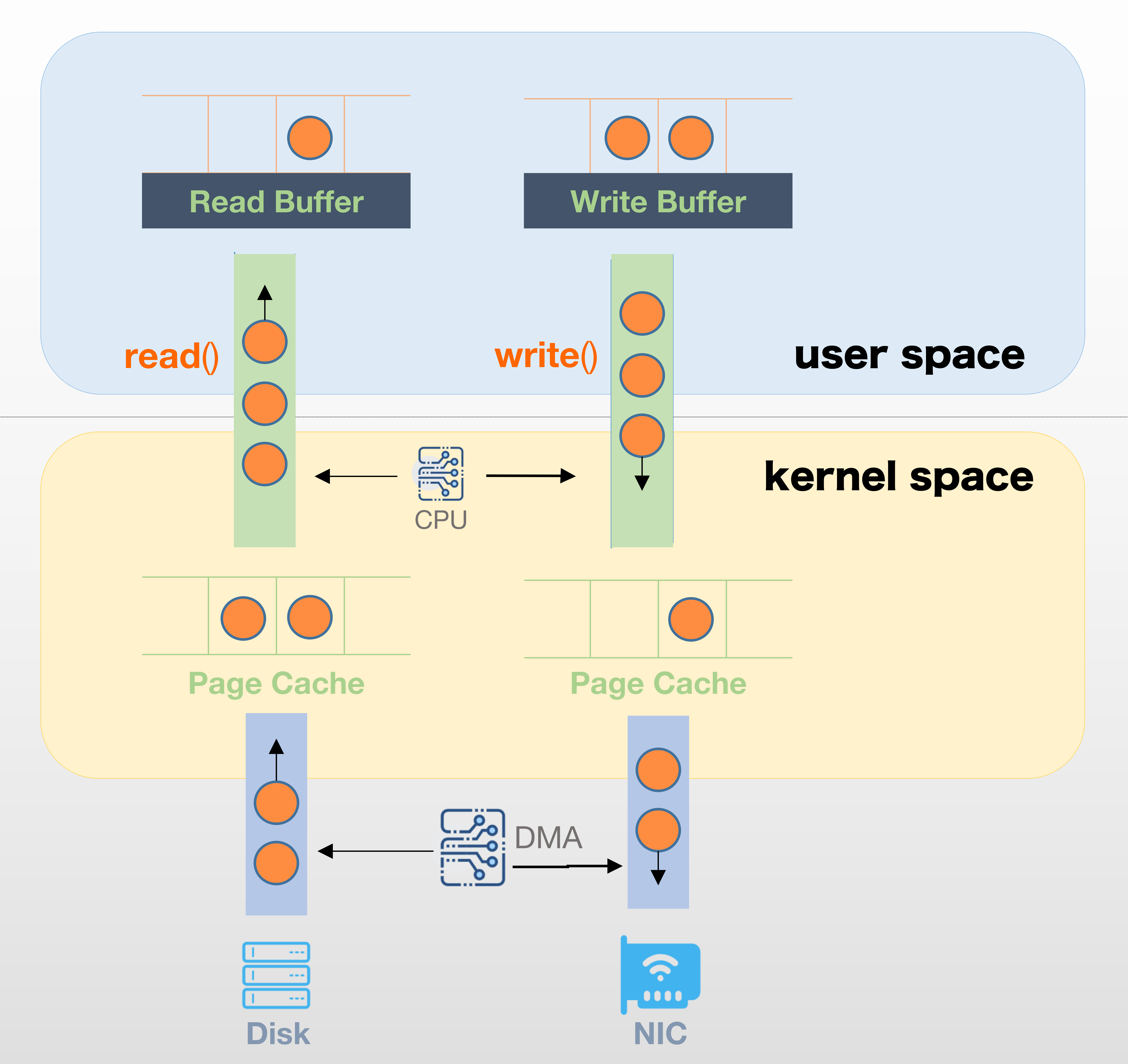
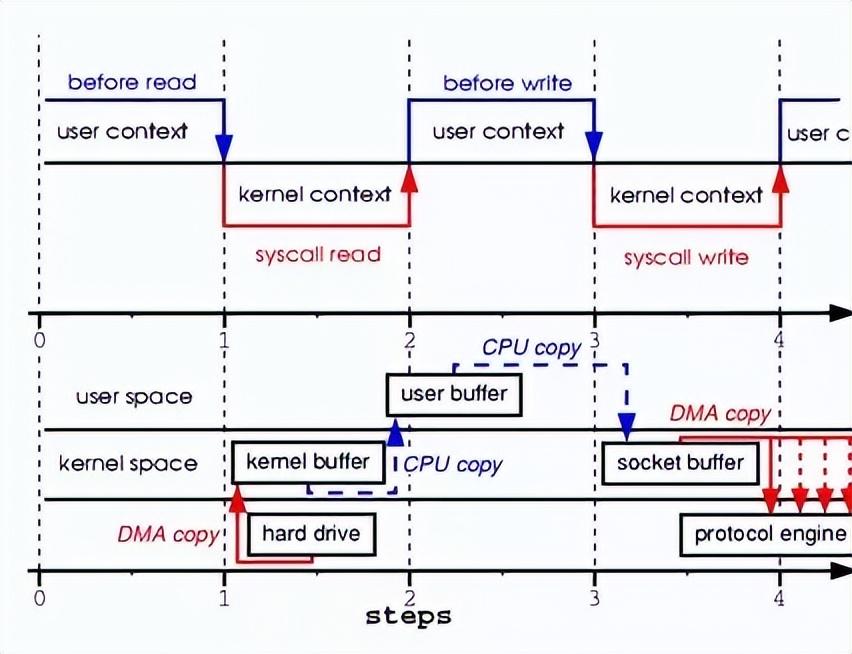
DMA = Direct Memeory Access (直接内存访问)
Memory Mappped I/O (内存映射 I/O)
#include <sys/mman.h>
/* POSIX.1-2001, POSIX.1-2008, SVr4, 4.4BSD */
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags,
int fd, off_t offset);
int munmap(void *addr, size_t length);
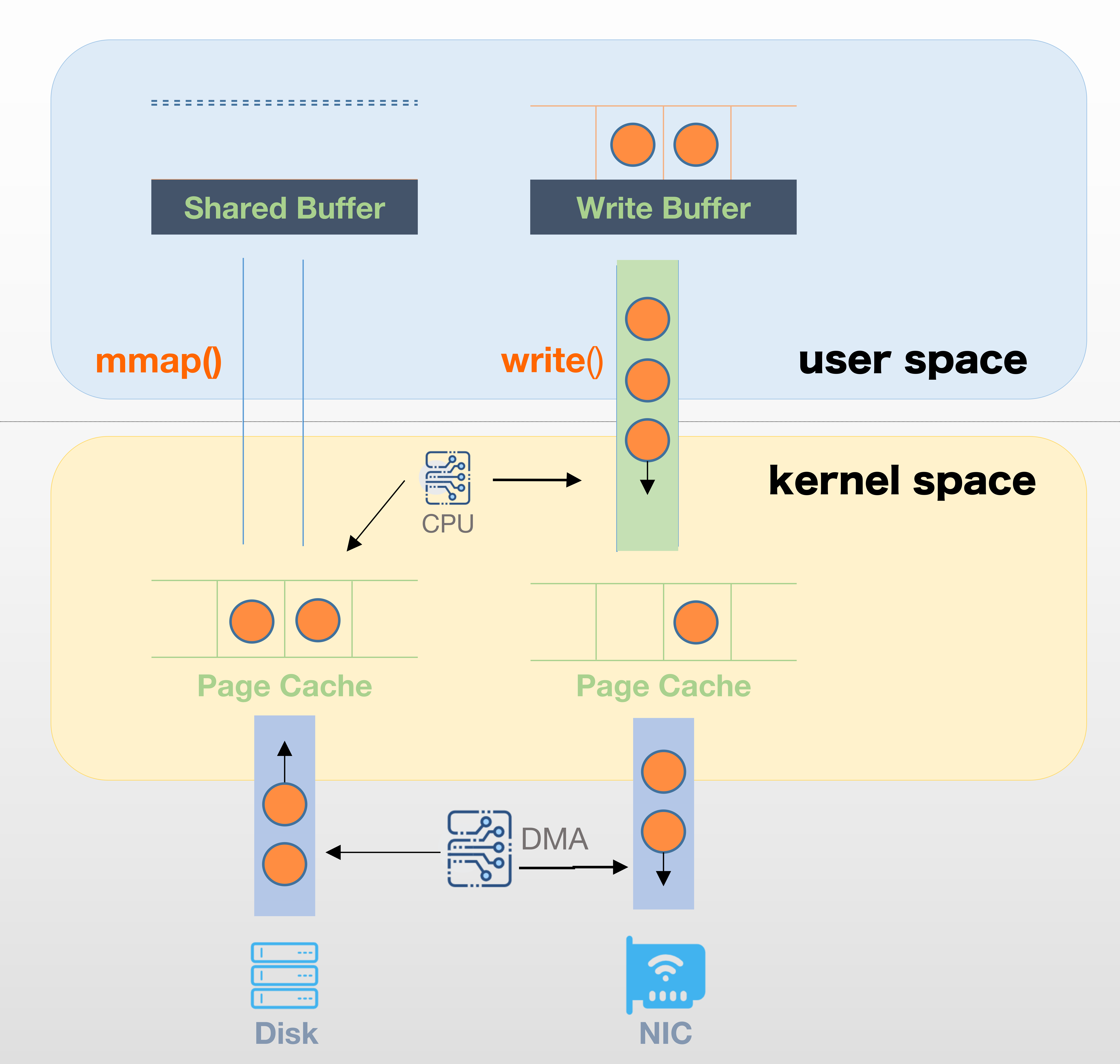
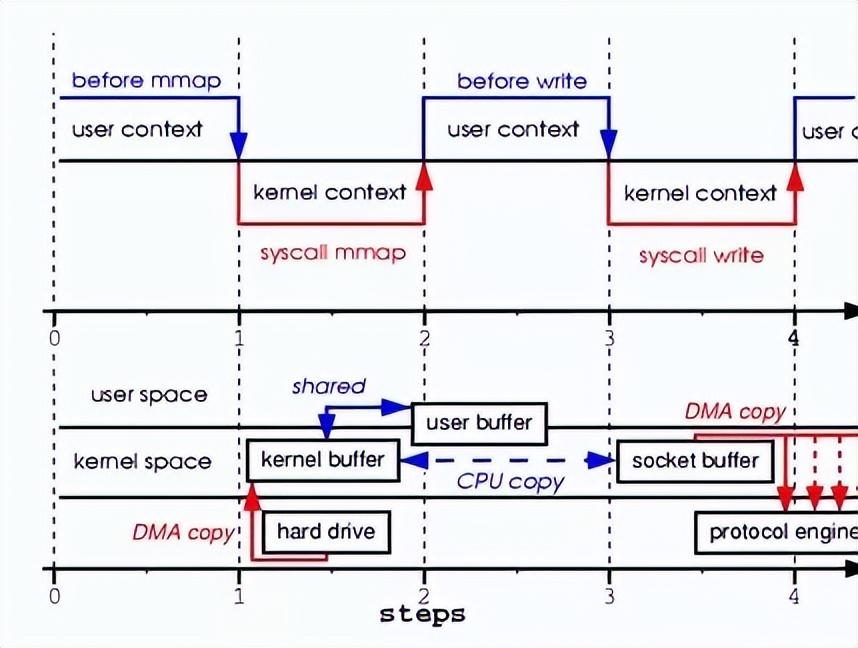
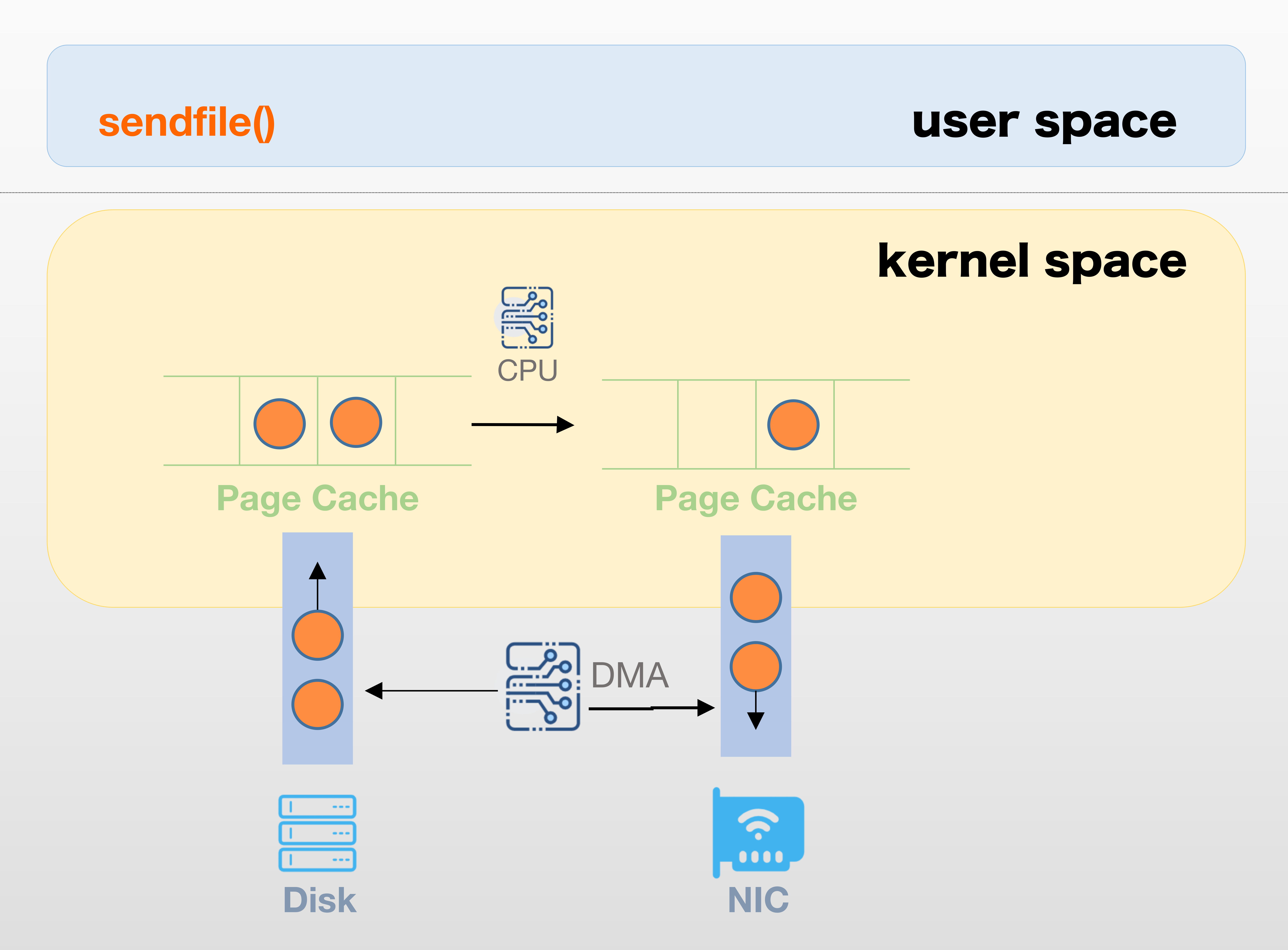
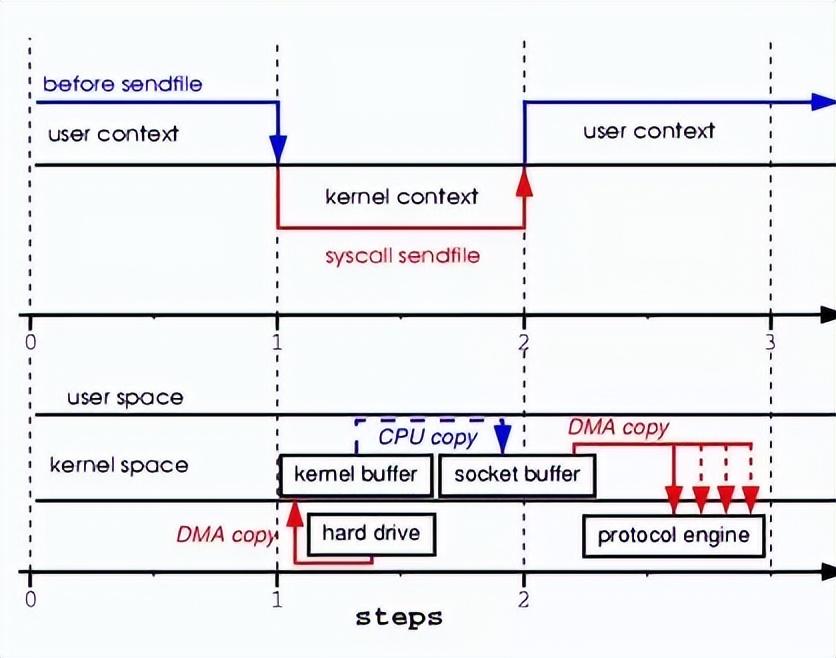
Sendfile
Since Linux 2.2.
#include <sys/sendfile.h>
/**
Since Linux *2.6.33*, `out_fd` can be any file.
If you plan to use `sendfile()` for sending files to a TCP socket,
but need to send some header data in front of the file contents,
you will find it useful to employ the `TCP_CORK` option,
to minimize the number of packets and to tune performance.
This option can be combined with `TCP_NODELAY` only since Linux *2.5.71*.
The original Linux `sendfile()` system call was not designed to handle large file offsets.
Consequently, Linux 2.4 added `sendfile64()`, with a wider type for the `offset` argument.
The glibc `sendfile()` wrapper function transparently deals with the kernel differences.
*/
ssize_t sendfile(int out_fd, int in_fd, off_t *offset, size_t count);
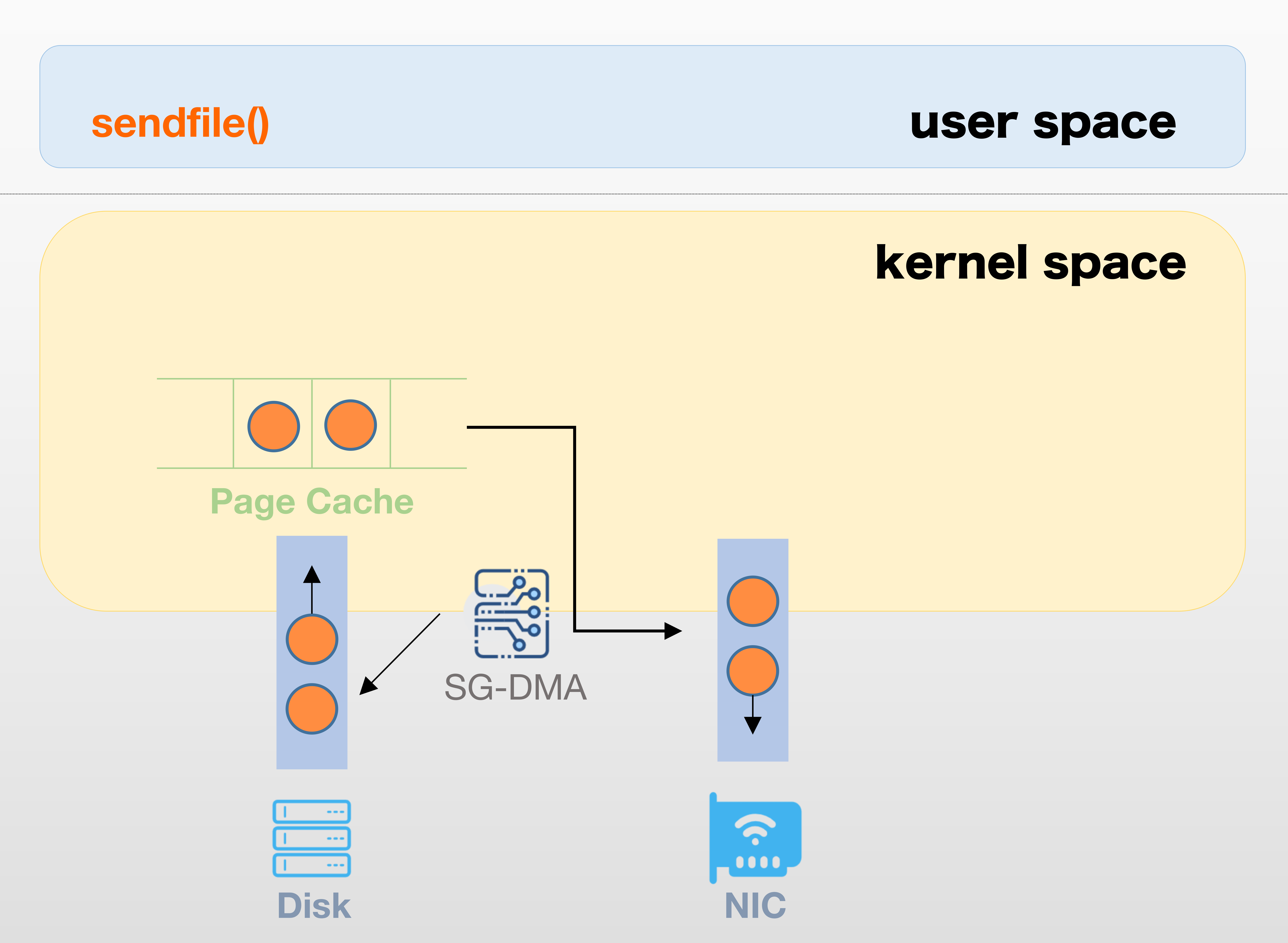
SG-DMA
SG-DMA = Scatter-Gather Direct Memory Access
$ ethtool -k eth0 | grep scatter-gather
scatter-gather: on
Since Linux 2.4:
Use Cases
- Nginx
- Kafka
Nginx
http {
...
sendfile on;
...
}
# turn on `aio` (async io) + `directio` when file size is greater than 1024MB;
# otherwise, turn on `sendfile`
location /bigfile/ {
sendfile on;
aio on;
directio 1024m;
}
References
- Book: Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment, 3rd Edition. (2013)
read(2) - Linux Programmer’s Manualwrite(2) - Linux Programmer’s Manualmmap(2) - Linux Programmer’s Manualsendfile(2) - Linux Programmer’s Manual